SIERRA HOUSES
The devastating impact of forest fires in the United States has been felt most critically in small, rural communities built on the edges of our forests. When the Dixie Fire ripped through the town of Greenville, California in August of 2021, almost 1,000 structures were completely lost, including 660 homes.
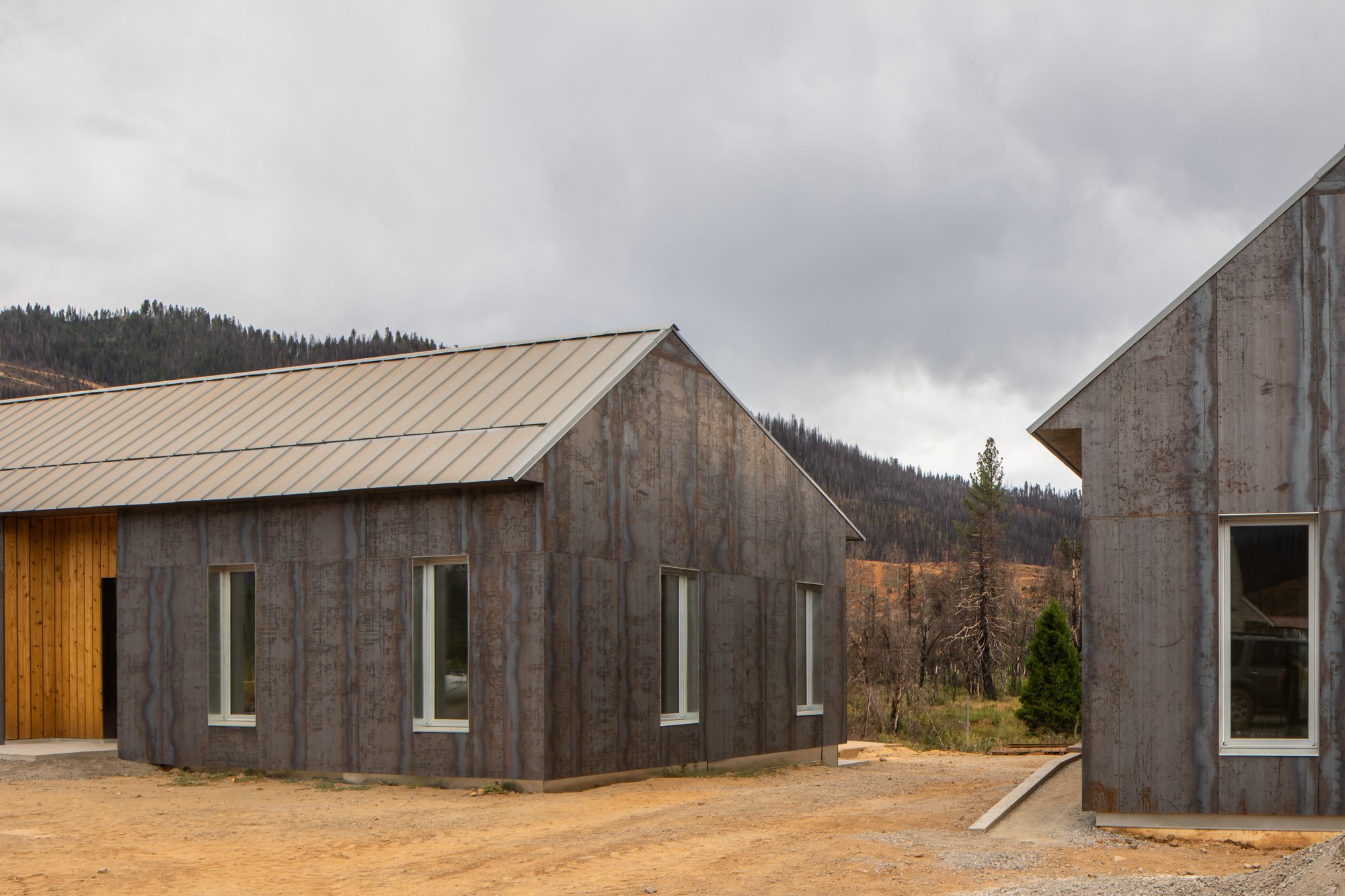
Working with the locally based Sierra Institute for Community and Environment, atelierjones developed three mass timber modular prototype houses to help advance a sustainable, fire-safe vision for community rebuilding.
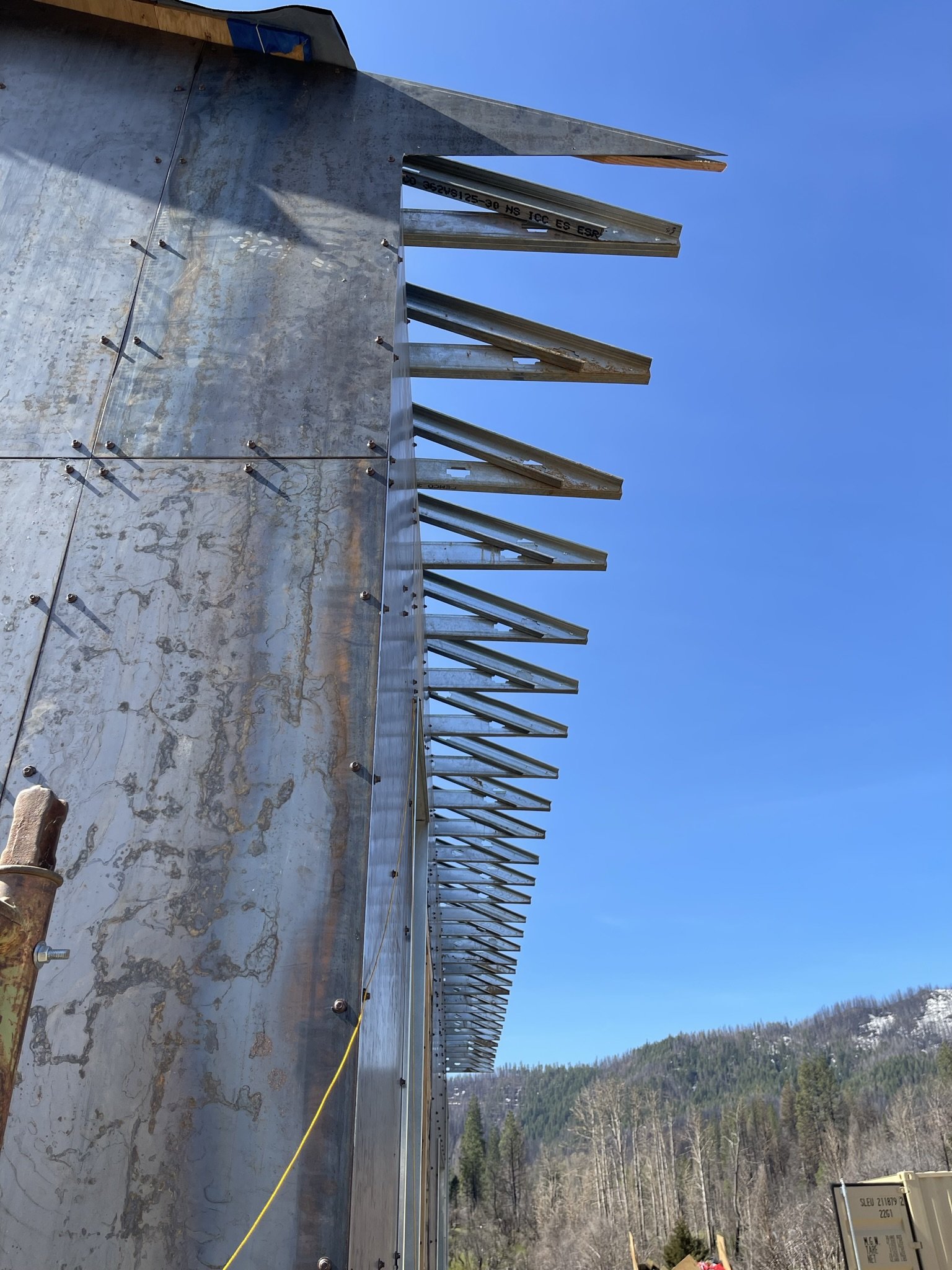
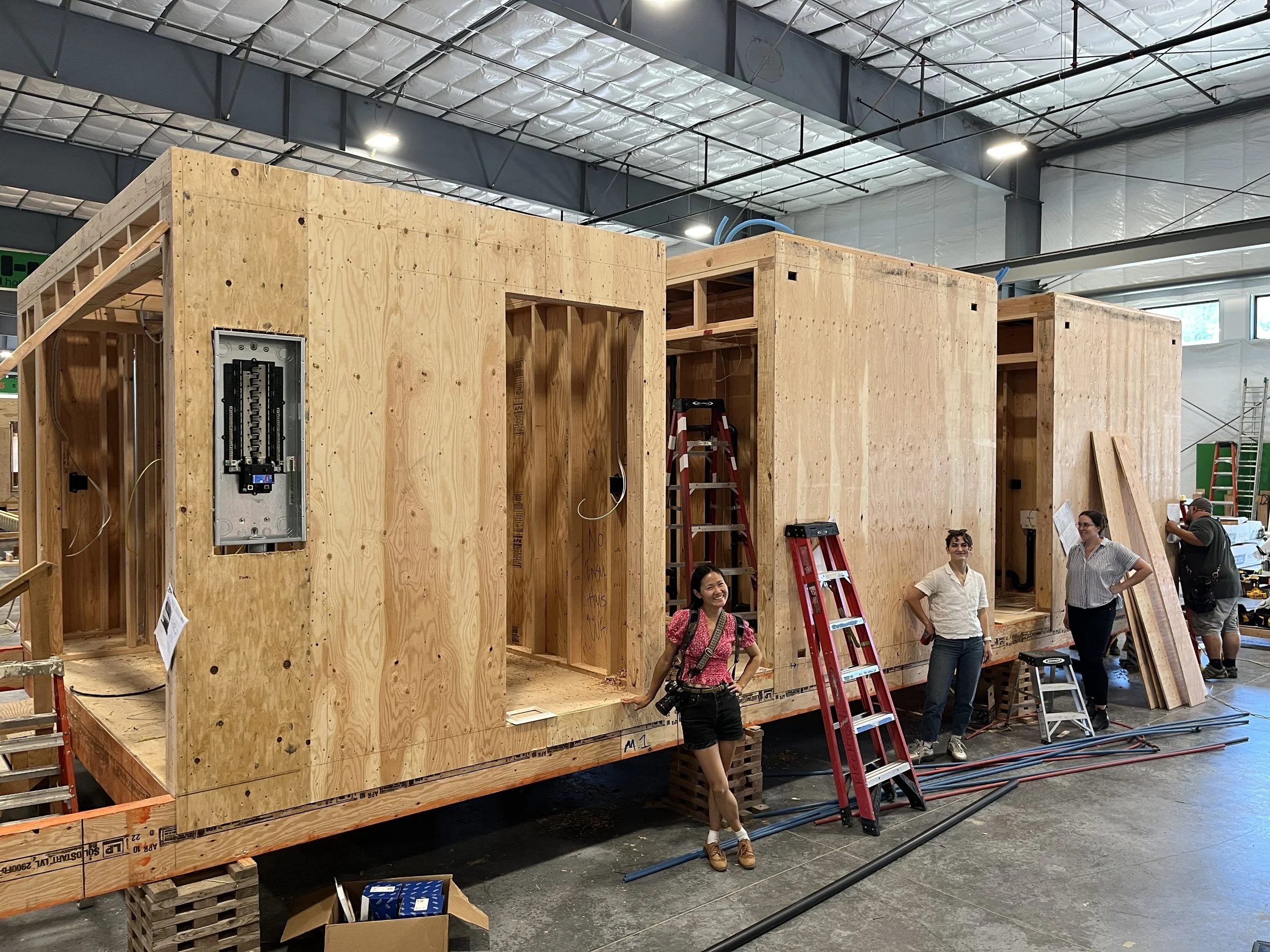
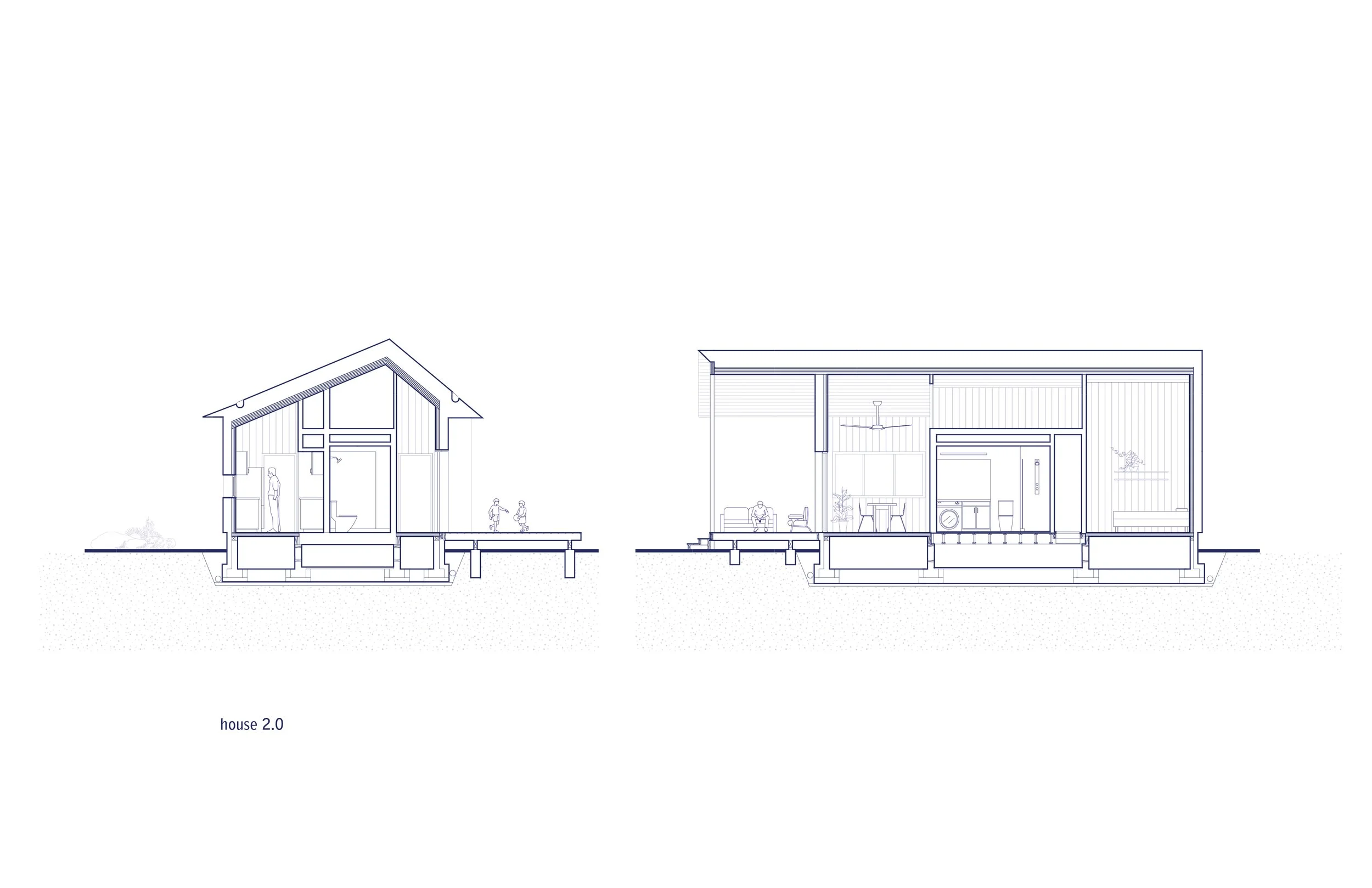
To meet the challenge of affordable, rapid, and sustainable rebuilding, the houses were designed to take full advantage of prefabrication. The houses were each designed around a modular wet core containing kitchen, bathroom, mechanical, and electrical systems. These cores could be fabricated off site then shipped in one piece, while Cross-Laminated Timber walls, floors, and roofs would arrive as flat-pack, pre-cut elements to be assembled around these central cores. This approach allowed the structures to be erected rapidly on site with only a few hands, and can be deployed at scale even when minimal local labor is available.
Although timber may seem like a contradictory choice in designing for fire resilience, the mass of mass timber means it is highly resistant to flame spread, and provides much greater resistance than conventional light frame construction. Following the Wildland Urban Interface design guidelines, the houses are further hardened with metal cladding, and designed so as not to catch loose embers or flammable plant material.
When sourced intentionally, mass timber supports resilient ecologies and reduces future fire risk by promoting forest health through good forest management practices.
For the next generation of fire-rebuild homes, the Sierra Institute is developing the infrastructure to produce Cross-Laminated Timber locally, allowing these structures to play a role in rebuilding not just the physical community, but the local economy as well.
A key element of our design principles is reducing both embodied carbon and operational carbon to move toward a carbon neutral future. Embodied carbon is primarily reduced through material sourcing and selection. High carbon materials are minimized to where they are most valuable, in light-weight foundations and in the fire-resistant cladding.
Operational Carbon is reduced through passive house design principles, which work hand in hand with mass timber construction and WUI guidelines. The well-sited forms of the homes are compact, with airtight, highly insulated envelopes and high-quality windows. HEPA filters and air-source heat pumps allow for occupant health and comfort even during California’s ever growing fire season. Reducing operational carbon also reduces cost for occupants, allowing residents to stay in their homes and stay in the community.
NBC News Bay Area - Greenville Rising from the Ashes 2 Years After Dixie Fire
2021–
Greenville, California
atelierjones: Susan Jones, Meghan Doring, Eleanor Lewis, Payton Narancic, Lenore Wan
COLLABORATORS
Developer: The Sierra Institute for Community and Environment
Contractor: Lights Creek Construction
Structural Engineering: Harriott Valentine Engineers
Mass Timber Strategy: Steve Marshall
Mass Timber Supplier/Fabricator: DR Johnson
Modular Fabricator: Method Homes
Photography: Lara Swimmer
AWARDS
2023 AIA Seattle Honor Awards - Award of Merit
2023 AIA Seattle Honor Awards - Young Voices Selection
PUBLICATION
Rising from the Ashes: Mass Timber Helps Resurrect a Fire-Torn Town in Rural California - Sarah Amelar, Architectural Record, 2023
atelierjones brings hope and new homes to fire-ravaged community in CA - Emma Hinchliffe, Daily Journal of Commerce, 2023
Building a Restorative, Climate Smart Future - WebsEdge Science, 2024
RELATED PROJECTS
CLT House
Roundhouse
R&D Modular